Ensuring Safety and Stability: The Significance of Electrical Grounding
Electrical grounding is an indispensable aspect of any
electrical system, crucial for ensuring safety, functionality, and durability
of equipment. This article delves into the essence of electrical grounding and
outlines effective techniques to establish a robust electrical grounding
system.
Understanding
Electrical Grounding
Electrical grounding entails connecting electrical
equipment, systems, or cables to the Earth or a reference point, providing a
secure pathway for electrical currents.
Purpose of Electrical
Grounding
The primary objectives of electrical grounding include:
- Preventing electric shocks
- Safeguarding electrical equipment and
individuals
- Ensuring system stability
- Components of an Electrical Grounding System
Key components of an electrical grounding system comprise:
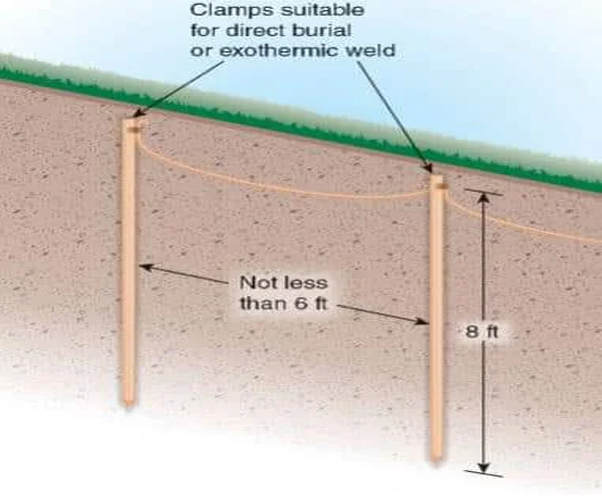
- Grounding Electrode: Connects physically to the
Earth, typically via rods, pipes, or plates.
- Grounding Conductor: Links the electrical system
to the grounding electrode.
- Grounding Bus: Central point where multiple
conductors converge, enhancing system efficiency.
Importance of
Electrical Grounding
Electrical grounding holds significance in various aspects:
- Provides a low-resistance path for fault
currents, averting electric shocks.
- Dissipates excess energy into the Earth,
safeguarding equipment.
- Establishes a stable voltage reference point,
ensuring reliable electrical performance.
- Minimizes electromagnetic interference,
preserving electronic signal integrity.
- Offers designated path for lightning discharge,
protecting equipment during storms.
Ensuring an Effective
Electrical Grounding System
To ensure efficacy of the grounding system, consider these
techniques:
- Ensure quality of electrode material and soil resistivity
during installation.
- Periodically inspect components for corrosion or
degradation, addressing issues promptly.
- Utilize low-resistance materials to enhance
fault current dissipation.
- Implement centralized grounding bus bar for
improved system performance.
- Introduce isolation measures to facilitate
unwanted current dissipation.
- Establish dedicated grounding paths for
sensitive equipment to mitigate interference.
- Incorporate isolation transformers to add an
extra layer of equipment protection.
Implementation Considerations
When implementing an electrical grounding system:
- Adhere to electrical codes and standards, particularly NEC (National Electrical Code).
- Stay updated with latest codes and standards for enhanced safety measures.
- Engage qualified electrical personnel for any electrical work.
- Seek professional advice for repair, modification, or dismantling of grounding systems.
Conclusion
Electrical grounding is not only a technical requirement but a fundamental aspect of electrical safety. By adhering to safe implementation practices, complying with safety measures, and contributing to an effective grounding system, individuals and equipment can be safeguarded against unwanted electrical currents, ensuring a secure and stable electrical environment.





.png)







